The Journey of Renewable Energy: From Water Wheels to Solar Panels

The quest for renewable energy is not a modern phenomenon. For centuries, humanity has harnessed the power of nature to perform work, long before the term 'renewable energy' entered our lexicon. From the flowing rivers that turned water wheels to the sophisticated solar panels capturing the sun's rays, the journey of renewable energy is a testament to human innovation and our relationship with the environment. This article traces the evolution of renewable energy technologies, exploring the milestones that have defined this journey and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Ancient Innovations and Early Adaptations
Water Wheels: The Birth of Mechanical Energy
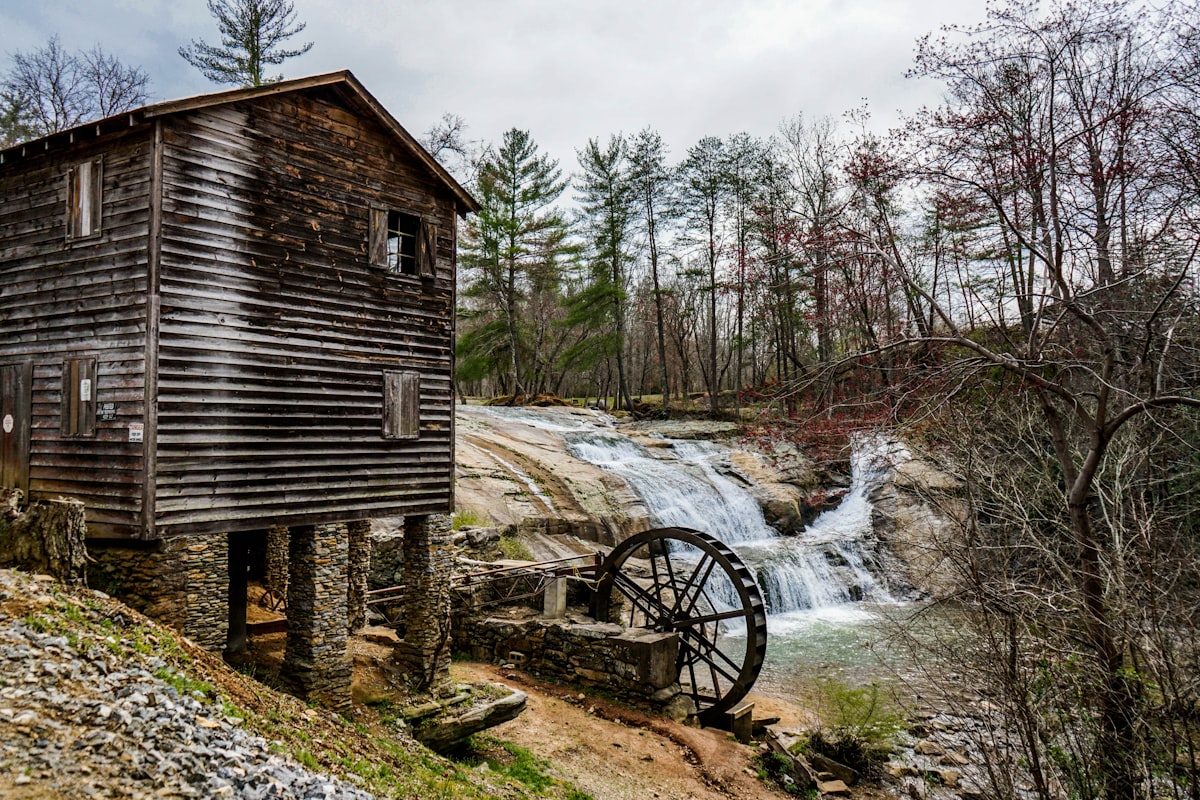
The water wheel is one of the earliest known devices to convert natural energy into mechanical energy. Dating back to around 400 B.C., ancient civilizations such as the Greeks and Romans utilized water wheels for grinding wheat into flour. These early wheels were simple structures placed in flowing streams or rivers, capturing the kinetic energy of water to turn a millstone.
- 400 B.C. - Early water wheels appear in Greece and other parts of the ancient world.
- Middle Ages - Water wheels spread throughout Europe, powering various industries.
Windmills: Harnessing the Breeze
Following the water wheel, windmills emerged as another form of renewable energy. First recorded in Persia around 500-900 A.D., windmills were used for similar purposes, such as grinding grain and later pumping water. The technology spread to Europe in the Middle Ages, where it became a common sight in countries like the Netherlands.
- 500-900 A.D. - The first windmills are developed in Persia.
- 12th Century - Windmill technology reaches Europe.
The Industrial Revolution and Fossil Fuels
The Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift away from renewable energy sources as coal became the dominant energy source. The development of the steam engine and its subsequent adoption across various industries led to an increased demand for fossil fuels, overshadowing the use of renewables for over a century.
- 18th Century - The Industrial Revolution begins, powered by coal.
The Resurgence of Renewable Energy
The Birth of Hydroelectric Power
In the late 19th century, the potential of water power was revisited with the development of hydroelectric technology. The first hydroelectric power plant was built at Niagara Falls in 1879, marking the beginning of large-scale electrical energy production from renewable sources.
- 1879 - The first hydroelectric power plant is established at Niagara Falls.
The Rise of Wind and Solar Power
The oil crises of the 1970s prompted a renewed interest in renewable energy technologies. Wind and solar power, in particular, began to gain traction as viable alternatives to fossil fuels. The first wind turbines were constructed, and photovoltaic (solar) cells were developed, initially for space applications before being adapted for terrestrial use.
- 1970s - The oil crises lead to a resurgence of interest in renewable energy.
- 1980s - Wind turbines become more common, and solar panels begin to appear on rooftops.
Advancements in Solar Technology
Solar panels have come a long way since their inception. The efficiency of photovoltaic cells has increased dramatically, making solar power more accessible and cost-effective. Innovations such as concentrated solar power (CSP) and solar thermal energy have expanded the applications of solar technology.
- 1990s-Present - Improvements in solar cell efficiency and the development of CSP.
Modern Challenges and Opportunities
Grid Integration and Storage
One of the main challenges facing renewable energy today is integration into the existing power grid. Renewable sources like wind and solar are intermittent, meaning they do not produce energy consistently. Advances in energy storage, such as battery technology, are crucial for overcoming this hurdle.
Policy and Investment
Government policies and investment play a significant role in the adoption of renewable energy. Incentives for renewable energy development, such as subsidies and tax credits, can significantly influence the market. International agreements like the Paris Climate Accord also drive the push for renewables.
Technological Innovation
Continued technological innovation is essential for the future of renewable energy. Emerging technologies like wave and tidal power, as well as ongoing improvements in wind and solar efficiency, hold promise for a more sustainable energy landscape.
Conclusion
The journey of renewable energy, from the ancient water wheels to the sophisticated solar panels of today, reflects humanity's enduring ingenuity and adaptability. Despite the challenges, the transition to renewable energy sources is a critical component of our global effort to combat climate change and create a sustainable future. As technology advances and the world increasingly recognizes the importance of renewable energy, the story of this journey will continue to evolve, shaping the way we live and power our lives for generations to come.