The Future of Data Transfer: Li-Fi Technology
In today's digital age, the demand for faster and more efficient data transfer is increasing exponentially. Traditional wireless communication technologies like Wi-Fi have reached their limits, leading to the emergence of a new and promising technology known as Li-Fi. Li-Fi, short for Light Fidelity

Introduction
In today's digital age, the demand for faster and more efficient data transfer is increasing exponentially. Traditional wireless communication technologies like Wi-Fi have reached their limits, leading to the emergence of a new and promising technology known as Li-Fi. Li-Fi, short for Light Fidelity, is a wireless communication technology that uses light to transmit data. In this article, we will explore the potential of Li-Fi, its underlying technology and its impact on the future of data transfer.
How Li-Fi Works
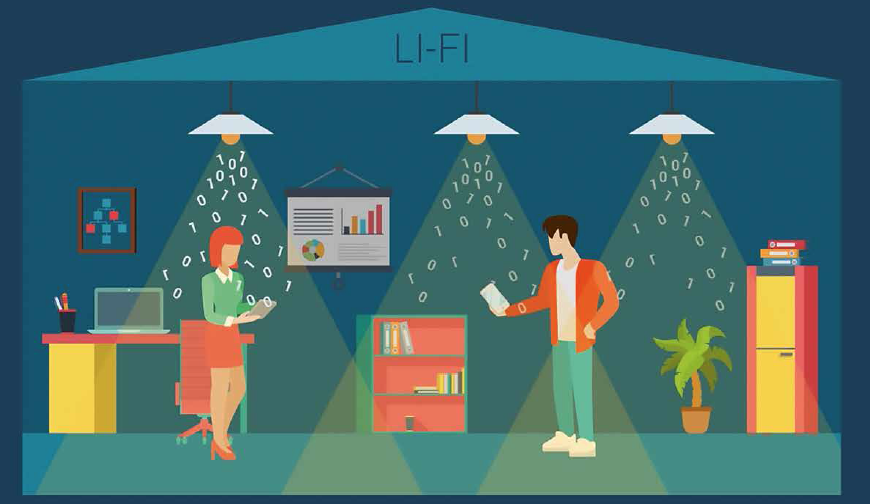
Li-Fi utilises visible light communication (VLC) to transmit data. It works by modulating the intensity of light emitted by LED bulbs at high speeds, which is then received and decoded by a photodetector. This modulation happens so rapidly that it is imperceptible to the human eye.
At the heart of Li-Fi technology is the concept of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). OFDM is a modulation technique that divides the available spectrum into multiple subcarriers, each carrying a portion of the data. By using different frequencies for each subcarrier, OFDM enables simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams. This allows for higher data rates and improved spectral efficiency.
The data transfer in Li-Fi occurs through light waves, which have a much higher frequency than radio waves used in traditional Wi-Fi. This higher frequency allows for significantly faster data transfer rates, potentially reaching speeds of several gigabits per second. Moreover, since light cannot penetrate walls, Li-Fi offers a more secure means of communication, making it ideal for applications that require high levels of data security.
Advantages of Li-Fi
Speed
One of the key advantages of Li-Fi is its incredible speed. With the potential to achieve speeds hundreds of times faster than Wi-Fi, Li-Fi has the ability to revolutionise data transfer. This high-speed capability opens up new possibilities for applications such as real-time video streaming, large file transfers and data-intensive tasks.
Bandwidth
Li-Fi leverages the vast amount of available spectrum in the visible light range, providing a virtually unlimited bandwidth for data transfer. This abundance of spectrum allows for more devices to connect simultaneously without experiencing congestion or degradation in performance.
Security
As mentioned earlier, Li-Fi offers enhanced security compared to Wi-Fi. Since light cannot pass through walls, it becomes much more difficult for unauthorised users to intercept or access the data being transmitted. This makes Li-Fi a compelling option for applications that require high levels of data security, such as military communications, financial transactions and healthcare systems.
Availability
Another advantage of Li-Fi is its availability. Since LED bulbs are already widely used for lighting purposes, implementing Li-Fi technology can be as simple as replacing existing bulbs with Li-Fi-enabled ones. This means that Li-Fi can be easily deployed in existing infrastructure without the need for significant additional investment.
Potential Applications of Li-Fi
The potential applications of Li-Fi are vast and diverse. Here are a few areas where Li-Fi is expected to make a significant impact:
Internet of Things (IoT)
Li-Fi can play a crucial role in the development of the IoT. With its high-speed data transfer capabilities and enhanced security, Li-Fi can enable seamless communication between IoT devices, allowing for faster and more efficient data exchange. This can lead to advancements in smart homes, smart cities and industrial automation.
Healthcare
Li-Fi can revolutionise healthcare by enabling real-time monitoring and communication between medical devices. For example, Li-Fi can be used to transmit patient data from wearable devices to healthcare professionals, allowing for faster and more accurate diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, Li-Fi can provide high-speed connectivity in hospitals, enabling quick access to patient records and facilitating telemedicine applications.
Transportation
In the transportation sector, Li-Fi can enhance communication between vehicles, traffic lights and infrastructure. This can lead to improved traffic management, increased safety and the development of autonomous vehicles. Li-Fi can enable vehicles to exchange data in real-time, facilitating cooperative collision avoidance, traffic flow optimisation and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication.
Retail and Hospitality
Li-Fi can enhance the customer experience in retail and hospitality settings. For instance, Li-Fi-enabled lighting can transmit product information, promotional offers and personalised recommendations directly to customers' smartphones, creating a more immersive and interactive shopping experience. In hotels, Li-Fi can provide high-speed internet access in rooms, conference areas and public spaces, ensuring a seamless connectivity experience for guests.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While Li-Fi holds immense potential, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed. One major challenge is the limited range of Li-Fi compared to Wi-Fi. Light waves can only travel a few meters, which means that multiple Li-Fi access points may be required to provide seamless coverage in large areas. Additionally, obstacles such as walls and physical obstructions can hinder the transmission of light signals.
To overcome these challenges, researchers are exploring various techniques such as beamforming, multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems and hybrid Li-Fi/Wi-Fi networks. These techniques aim to improve the range, reliability and coverage of Li-Fi systems, making them more practical for widespread deployment.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see advancements in Li-Fi range, reliability and interoperability with existing wireless communication technologies. Standardisation efforts are also underway to ensure compatibility and interoperability between different Li-Fi devices and networks.
In conclusion, Li-Fi technology has the potential to revolutionise data transfer by providing faster speeds, enhanced security and virtually unlimited bandwidth. With its diverse applications and ongoing advancements, Li-Fi is poised to shape the future of data transfer and enable a wide range of innovative solutions in various industries. While there are still challenges to overcome, the future of Li-Fi looks promising and we can expect to see its widespread adoption in the coming years.