The Age of Space Exploration: From Sputnik to SpaceX
The narrative of human space exploration is a saga of innovation, resilience and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. From the beep of Sputnik orbiting the Earth to the roar of

Introduction
The narrative of human space exploration is a saga of innovation, resilience and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. From the beep of Sputnik orbiting the Earth to the roar of SpaceX's Falcon rockets, each chapter has been marked by groundbreaking developments that have redefined our relationship with the cosmos. This article delves into the evolution of space exploration technologies, highlighting the key advancements and the challenges overcome along the way.
The Dawn of the Space Age: Sputnik
Sputnik: The First Artificial Satellite
On October 4, 1957, the world was introduced to the space age when the Soviet Union successfully launched Sputnik 1. This 58 cm diameter polished metal sphere, with its iconic beeping signal, not only transmitted data about the ionosphere but also sent a clear message about the Soviet Union's technological capabilities.
Technological Significance of Sputnik
Sputnik's success was based on the R-7 rocket, an intercontinental ballistic missile repurposed for spaceflight. The satellite itself carried only a simple radio transmitter, but its implications were profound, igniting the space race and setting the stage for future technological advancements.
The Response: NASA and the Apollo Program
Galvanized by the Soviet achievement, the United States founded NASA and committed to winning the space race. This culminated in the Apollo program, an audacious plan to land humans on the Moon.
The Moon Landing
The Apollo 11 mission's success in 1969 was the result of a massive technological undertaking, involving the Saturn V rocket, the most powerful rocket ever built. The Lunar Module, a spacecraft designed specifically for lunar surface operations, allowed Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin to make history as they took "one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind."
The Shuttle Era
The Space Shuttle: Reusability in Space
The Space Shuttle, officially called the Space Transportation System (STS), represented a new philosophy in space travel: reusability. First launched in 1981 with the orbiter Columbia, the Shuttle could carry astronauts and cargo to orbit and return to Earth to be flown again.
Technological Advances and Challenges
The Shuttle's design included many innovations, such as thermal protection tiles and the first use of a computerized fly-by-wire digital flight control system. However, the complexities of its design also posed risks, tragically realized in the Challenger and Columbia disasters. These events prompted intense scrutiny and improvements in safety protocols.
The International Space Station
Collaboration in Orbit
The ISS is a symbol of international partnership, involving space agencies from the United States (NASA), Russia (Roscosmos), Europe (ESA), Japan (JAXA) and Canada (CSA). It serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory where scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics and other fields.
Technological Milestones of the ISS
The ISS has been a platform for numerous technological firsts. For example, the Advanced Resistive Exercise Device (ARED) allows astronauts to maintain muscle strength in microgravity. The Water Recovery System recycles fluids, including urine, into potable water—a crucial technology for long-duration space missions.
The Rise of Commercial Spaceflight
SpaceX and the New Space Economy
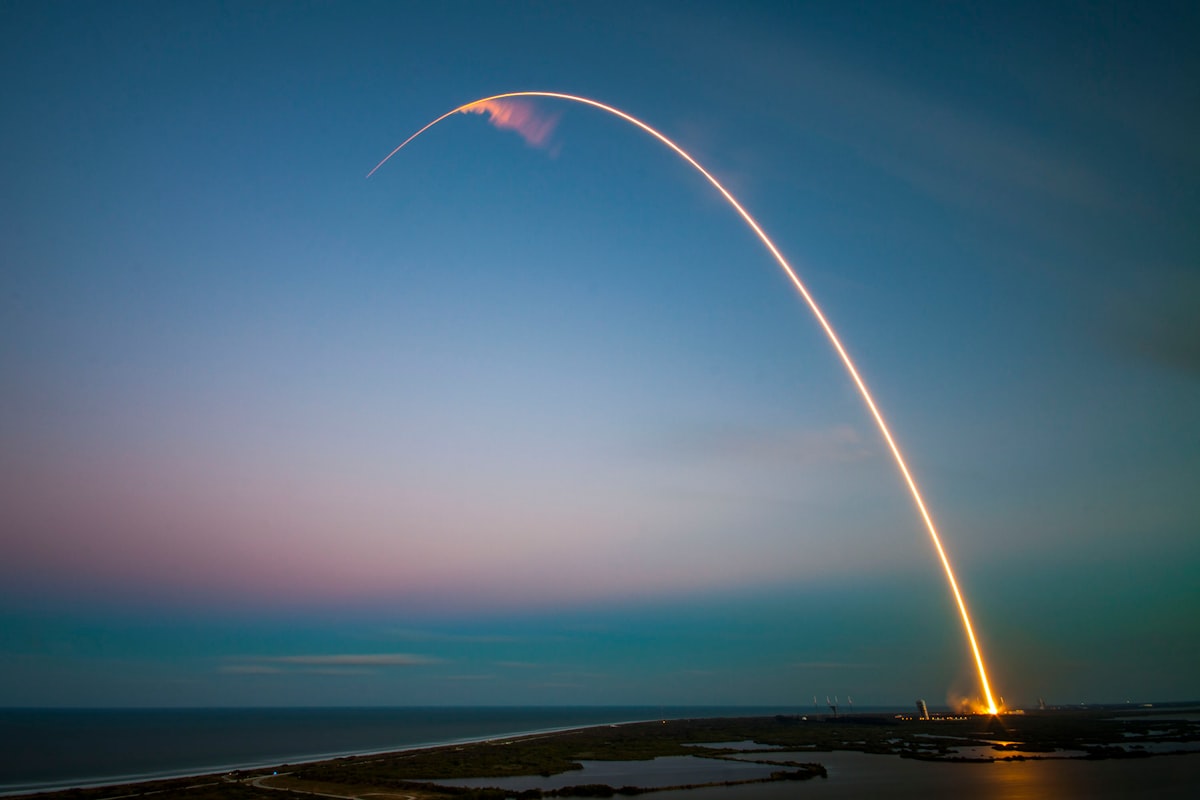
Elon Musk's SpaceX has disrupted the space industry with its bold vision and innovative technologies. By focusing on cost reduction and reusability, SpaceX has opened new possibilities for space travel and exploration.
Reusable Rockets and Commercial Cargo
SpaceX's Falcon 1 was the first privately developed liquid-fueled rocket to reach orbit in 2008. The Falcon 9, with its reusable first stage, has become a workhorse for satellite launches, ISS resupply missions and even crewed flights. The Dragon cargo spacecraft, which first docked with the ISS in 2012, was a milestone for commercial spaceflight.
Technological Innovations by SpaceX
SpaceX's achievements include the first propulsive landing for an orbital rocket (Falcon 9 in 2015), the first reuse of an orbital rocket (Falcon 9 in 2017) and the development of the Crew Dragon, which restored American capability to send astronauts to space from U.S. soil.
Starship: The Next Step
The Starship system represents SpaceX's ambition to make human life interplanetary. With a fully reusable design and the ability to carry up to 100 passengers, Starship aims to reduce the cost of space travel even further. Its first orbital tests are eagerly anticipated by the space community.
Conclusion
The age of space exploration has been a journey of extraordinary achievements and formidable challenges. From the pioneering launch of Sputnik to the groundbreaking innovations of SpaceX, each step has built upon the last, propelling humanity further into the final frontier. As we stand at the threshold of a new era in space exploration, we look back at the technological marvels that have brought us here and forward to the possibilities that await among the stars.